This page describes the threat model of Ledger signers (i.e. hardware products). It lists the main security objectives the devices intend to fulfill, then describes the security mechanisms implemented to achieve these objectives.
Security Objectives
The main security objective of Ledger signers is to provide physical and logical security to users' funds.
Seed & Key Confidentiality
Guarantee the confidentiality of user seeds and private keys.
User Consent
Ensure the use of digital assets is performed under user consent, preventing attackers from misleading users.
Genuineness
Provide a mechanism allowing users to verify that their device is genuine.
Privacy
Protect users' privacy and prevent unique identification of users.
Firmware Protection
Protect the confidentiality of the firmware and the IP of the Secure Element.
Definitions
Roles
End User
The owner of a Ledger signer with physical access to it.
Firmware Developer
Ledger employees who develop the OS and its cryptographic library.
App Developer
Anyone who develops apps running on top of BOLOS.
HSM
Hardware Security Modules that check device genuineness and perform privileged operations.
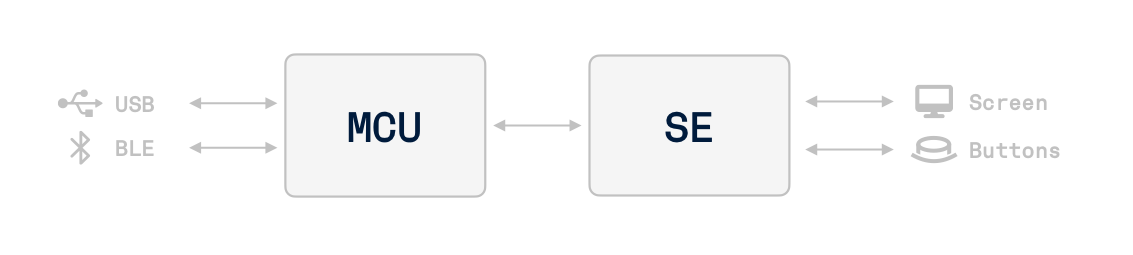
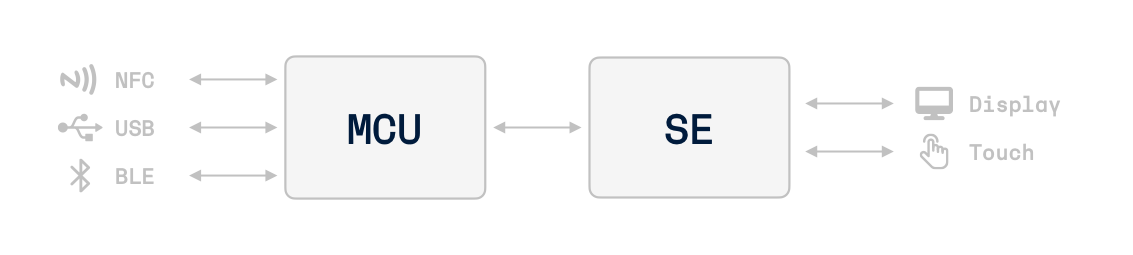
High Level Architecture
Ledger signers are composed of:
- A Secure Element (ST33 for Nano S Plus, Nano X, Nano Gen5, Stax and Flex)
- A general purpose MCU (STM32F042 for Nano S Plus, STM32WB55 for Nano X, STM32WB35 for Nano Gen5 and Stax/Flex)
- A NFC communication chip (ST25R3916 for Stax and Flex; ST21NFCLWLF for Nano Gen5)
- External peripherals: screen, buttons
Current product models include Nano S Plus, Nano X, Nano Gen5, Stax, and Flex.
Security Mechanisms
Several security mechanisms are implemented at different levels. Click on each mechanism to learn more.
| Level | Security Mechanism | Security Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Device | Genuineness | Genuineness |
| Secure Display and Inputs | Confidentiality of user seeds, User consent | |
| Physical Resistance | Confidentiality of user seeds, Confidentiality of the firmware | |
| OS | PIN Security Mechanism | Confidentiality of user seeds |
| Random Number Generation | Confidentiality of user seeds | |
| Confidentiality of Seed and Private Keys | Confidentiality of user seeds and private keys | |
| Confidentiality and Integrity | Confidentiality of the firmware | |
| Transport Security | Confidentiality of the firmware | |
| App | Isolation | Confidentiality of private keys, User consent |
| User Consent | User consent |
